Motor nameplates provide essential information that ensures motors are installed and operated safely and in compliance with codes. As an inspector, understanding this information is crucial for verifying installations.
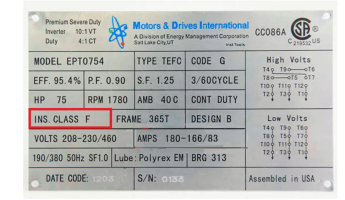
- Manufacturer & Model Number
- Purpose: Identifies the motor for reference and verification.
- Inspection Tip: Ensure the motor is listed and labeled by a recognized testing laboratory.
- Voltage (V)
- Purpose: Indicates the operating voltage.
- Inspection Tip: Verify that the motor's voltage rating matches the supply voltage.
- Full Load Amperage (FLA)
- Purpose: Shows the current drawn at full load.
- Inspection Tip: Use this to confirm correct sizing of conductors and overcurrent protection devices.
- Frequency (Hz)
- Purpose: Specifies the operating frequency.
- Inspection Tip: Ensure compatibility with the system frequency (typically 60 Hz in North America).
- Phase
- Purpose: Indicates single-phase or three-phase operation.
- Inspection Tip: Confirm that the motor's phase matches the supply.
- Horsepower (HP)
- Purpose: Denotes the motor's output power.
- Inspection Tip: Use this to verify appropriate application and load handling.
- Speed (RPM)
- Purpose: Shows the motor's rotational speed.
- Inspection Tip: Ensure the speed is suitable for the connected equipment.
- Service Factor (SF)
- Purpose: Indicates the motor's overload capacity.
- Inspection Tip: Recognize that a higher SF allows for occasional overloads; ensure it's not used continuously beyond its rating.
- Insulation Class
- Purpose: Defines the thermal tolerance of the motor's insulation.
- Inspection Tip: Confirm that the motor's insulation class is appropriate for the operating environment.
- Enclosure Type (e.g., TEFC, ODP)
- Purpose: Describes the motor's protection against environmental factors.
- Inspection Tip: Ensure the enclosure type suits the installation location (e.g., TEFC for dusty environments).
- Ambient Temperature Rating
- Purpose: Specifies the maximum ambient temperature for safe operation.
- Inspection Tip: Verify that the motor is suitable for the ambient conditions of the installation site.
- Duty Cycle
- Purpose: Indicates how long the motor can operate under specific conditions.
- Inspection Tip: Ensure the motor's duty rating aligns with its intended use.
- Code Letter
- Purpose: Provides information on the motor's starting current.
- Inspection Tip: Use this to assess the impact on the electrical system during startup.
- Design Letter
- Purpose: Defines the motor's torque and starting characteristics.
- Inspection Tip: Confirm that the motor's design is appropriate for the application.
- Efficiency
- Purpose: Shows how effectively the motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy.
- Inspection Tip: Higher efficiency motors reduce energy costs and heat generation.
Here's an example of a typical motor nameplate:

