Redefining 'Blueprints': The Digital Transformation in Architecture, Engineering, and Construction
Introduction
For over a century, the term 'blueprint' has been a staple in the lexicon of architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC). Synonymous with detailed plans used to guide the construction of buildings and infrastructure, blueprints were once pivotal to project management. However, the digital age has ushered in profound changes, rendering the traditional blueprint increasingly obsolete. This article explores the origins of blueprints, their evolution, and the modern terminology and technologies that have replaced them.
The Historical Context of Blueprints
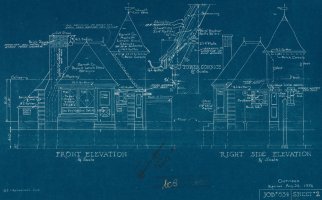
The blueprint process originated in the 19th century and became a fundamental method for reproducing technical and architectural drawings. The distinctive blue-and-white prints were produced through a chemical process known as cyanotype. The method was cost-effective and robust, making blueprints a ubiquitous tool in construction projects throughout the 20th century.
Transition to Digital Technologies
The late 20th century marked a pivotal shift with the advent of computer-aided design (CAD) software, revolutionizing how plans were drafted, shared, and stored. CAD offered numerous advantages over traditional blueprints, including:
- Precision and Flexibility: Digital files are more precise and can be easily updated without the need to produce new sets of prints.
- Efficiency: Digital files can be shared instantly across locations, reducing delays caused by physical document handling.
- Sustainability: Reducing paper use aligns with growing environmental sustainability goals within the industry.
Modern Terminology and Practices
With the shift from physical to digital, the terminology used in construction documentation has also evolved:
- Construction Documents (CDs): This term refers to the comprehensive set of drawings and specifications used to construct a building or infrastructure project.
- Project Drawings or Digital Plans: Often used interchangeably with CDs, these terms broadly encompass all digital designs and plans involved in a project.
- Design Deliverables: This focuses on the outputs during the design phase, including detailed drawings, models, and simulations.
- Contract Documents: These are legally binding documents that define the scope, responsibilities, and specifics of a construction project, ensuring all parties are aligned.
As technology continues to evolve, the AEC industry is likely to see further advancements that could redefine construction documentation even beyond current digital practices. Innovations like Building Information Modeling (BIM) and augmented reality (AR) are already beginning to enhance the way professionals interact with project data, offering dynamic, real-time updates and immersive interaction with design elements.
The iconic 'blueprint' holds a place in the nostalgic realms of architecture and engineering, yet the industry must continue to embrace and adapt to the digital methodologies that are shaping the future of construction. By adopting modern terminology and technologies, professionals in the AEC industry can ensure greater accuracy, efficiency, and collaboration in their projects.
