jar546
CBO
Understanding the ICC's Code Development and Adoption Process
The International Code Council (ICC) plays a crucial role in establishing building safety standards through its model codes, known as the International Codes or I-Codes. These codes are developed through a structured, transparent process that involves input from a wide range of stakeholders. This educational summary outlines how the ICC's code development process works, including the steps and timeframes involved.
References
The International Code Council (ICC) plays a crucial role in establishing building safety standards through its model codes, known as the International Codes or I-Codes. These codes are developed through a structured, transparent process that involves input from a wide range of stakeholders. This educational summary outlines how the ICC's code development process works, including the steps and timeframes involved.
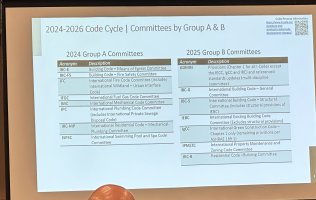
1. Code Development Cycle
The ICC updates its codes on a three-year cycle. This regular update schedule ensures that the codes reflect the latest advancements in technology, materials, and building practices, as well as lessons learned from recent events related to building safety.2. Steps in the Code Development Process
The code development process involves several key steps designed to encourage participation and ensure that the resulting codes serve the public interest.a. Submission of Code Change Proposals
- Timeframe: Proposal submission opens approximately 18 months before the publication of the new code edition.
- Process:
- Open Participation: Any interested party can submit proposals, including code officials, industry representatives, professionals, and the general public.
- Proposal Requirements: Each proposal must include the specific code section to be amended, the proposed change, and a reason statement explaining the rationale.
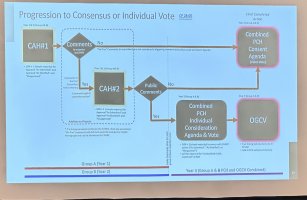
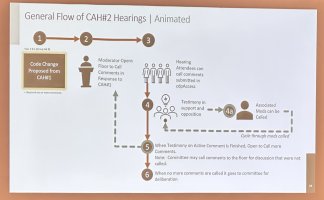
b. Committee Action Hearings
- Timeframe: Held in the spring of the first year of the cycle.
- Process:
- Review by Committees: Expert committees review each proposal. These committees are composed of volunteers with expertise in relevant areas.
- Public Testimony: Proponents and opponents of proposals can present their views.
- Committee Votes: Committees vote to approve, approve with modifications, or disapprove each proposal based on technical merit and public safety considerations.
c. Public Comment Period
- Timeframe: Following the Committee Action Hearings, a public comment period of around two months is provided.
- Process:
- Submission of Comments: Stakeholders can submit written comments on the committee's actions, suggesting further modifications or expressing support or opposition.
d. Public Comment Hearings
- Timeframe: Conducted in the fall of the first year.
- Process:
- Final Discussion: Proposals and public comments are discussed.
- Floor Actions: Modifications can be made based on the discussions.
- Voting: Attendees vote on each proposal, determining which changes move forward.
e. Online Governmental Consensus Vote
- Timeframe: Takes place shortly after the Public Comment Hearings.
- Process:
- Eligible Voters: Only ICC Governmental Member Voting Representatives (primarily code officials from governmental agencies) participate.
- Final Decision: Votes are cast online to finalize which code changes are approved for inclusion.
f. Publication of the New Codes
- Timeframe: The finalized codes are published in the spring of the second year.
- Process:
- Compilation: Approved changes are integrated into the new edition of the codes.
- Distribution: The updated codes are made available to jurisdictions and the public.
3. Adoption by Jurisdictions
While the ICC develops model codes, it does not have enforcement authority. Adoption and enforcement are the responsibilities of state and local governments.a. Review and Amendment
- Process:
- Evaluation: Jurisdictions review the new I-Codes to determine applicability.
- Customization: Amendments may be made to address specific regional needs, such as climate, geological conditions, or local practices.
b. Legislative or Regulatory Adoption
- Process:
- Formal Adoption: Jurisdictions adopt the codes through legislative or regulatory processes.
- Public Involvement: Some jurisdictions hold public hearings or comment periods before adoption.
c. Implementation
- Process:
- Effective Date: The adopted codes become law on a specified date.
- Enforcement: Local building departments enforce the codes through plan reviews, permits, and inspections.
d. Timeframes for Adoption
- Varies Widely:
- Some jurisdictions adopt new codes soon after publication to stay current.
- Others may delay adoption to allow time for training, public education, or to align with legislative schedules.
4. Benefits of the ICC's Process
- Inclusivity: The open process allows for participation from all interested parties.
- Transparency: Hearings and voting are conducted openly, and records are publicly available.
- Expertise: Committees consist of professionals with diverse backgrounds, ensuring well-rounded code development.
- Public Safety Focus: Final voting by governmental officials prioritizes the public interest over commercial or private interests.
5. Summary of Timeframes
- Year 1:
- January–March: Submission of code change proposals.
- April–May: Committee Action Hearings.
- June–July: Public comment period.
- October–November: Public Comment Hearings.
- November–December: Online Governmental Consensus Vote.
- Year 2:
- Early Year: Finalization and publication of new codes.
- Year 2–3:
- Variable: Adoption by jurisdictions.
6. Participation Opportunities
- Submitting Proposals: Anyone can propose changes to the codes.
- Attending Hearings: Open to the public for observation or participation.
- Voting: Governmental members vote in the final phase to ensure public interest is upheld.
TBCF Summary
The ICC's code development and adoption process is a collaborative effort that balances technical expertise, public safety, and the needs of various stakeholders. By understanding this process, professionals and interested parties can actively engage in shaping the building codes that impact safety, sustainability, and innovation in the construction industry. The structured timeline ensures that updates are systematic and that there is ample opportunity for input and review at each stage.References
- International Code Council Official Publications
- "The Code Development Process" – ICC Resource Materials
- "Participating in the ICC Code Development Process" – Building Safety Journal
- "Understanding Model Codes and Their Adoption" – Journal of Construction Regulation